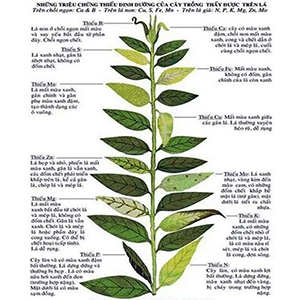
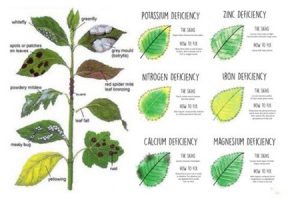
Table 1. The 14 elements essential for plant growth and their mobility and role within the plant.
|
Macronutrients
|
Symbol
|
Mobile in plant
|
Role in plant
|
Primary
|
Nitrogen
|
N
|
Yes
|
Formation of amino acids, vitamins and proteins; cell division
|
Phosphorous
|
P
|
Yes
|
Energy storage and transfer; cell growth; root and seed formation and growth; winter hardiness; water use
|
Potassium
|
K
|
Yes
|
Carbohydrate metabolism, breakdown and translocation; water efficiency; fruit formation; winter hardiness; disease resistance
|
Secondary
|
Calcium
|
Ca
|
No
|
Cell division and formation; nitrogen metabolism; translocation; fruit set
|
Magnesium
|
Mg
|
Yes
|
Chlorophyll production; phosphorus mobility; iron utilization; fruit maturation
|
Sulfur
|
S
|
No
|
Amino acids formation; enzyme and vitamin development; seed production; chlorophyll formation
|
Micronutrients
|
Boron
|
B
|
No
|
Pollen grain germination and tube growth; seed and cell wall formation; maturity promotion; sugar translocation
|
Chlorine
|
Cl
|
Yes
|
Role not well understood
|
Copper
|
Cu
|
No
|
Metabolic catalyst; functions in photosynthesis and reproduction; increases sugar; intensifies color; improves flavor
|
Iron
|
Fe
|
No
|
Chlorophyll formation; oxygen carrier; cell division and growth
|
Manganese
|
Mn
|
No
|
Involved in enzyme systems; aids chlorophyll synthesis; P and CA availability
|
Molybdenum
|
Mo
|
Yes
|
Nitrate reductase formation; converts inorganic phosphates to organic
|
Nickel
|
Ni
|
Yes
|
Nitrogen metabolism and fixation; disease tolerance
|
Zinc
|
Zn
|
No
|
Hormone and enzyme systems; chlorophyll production; carbohydrate, starch and seed formation
|